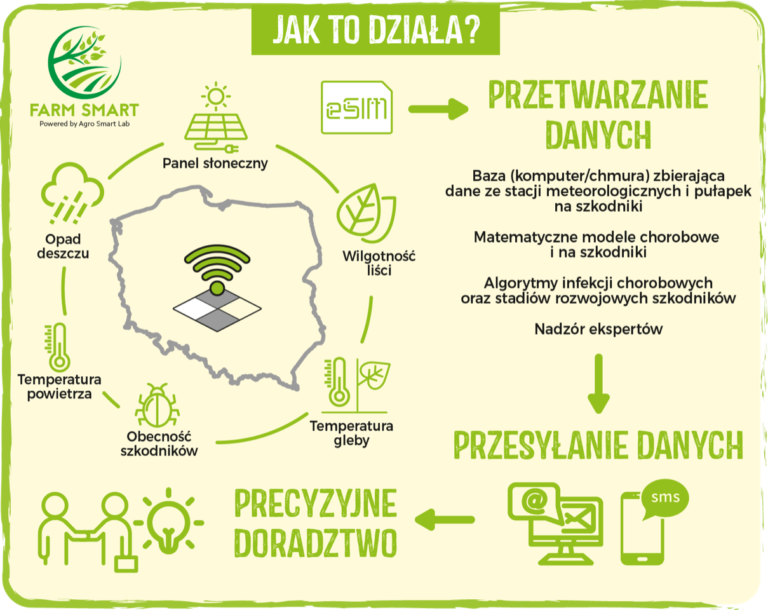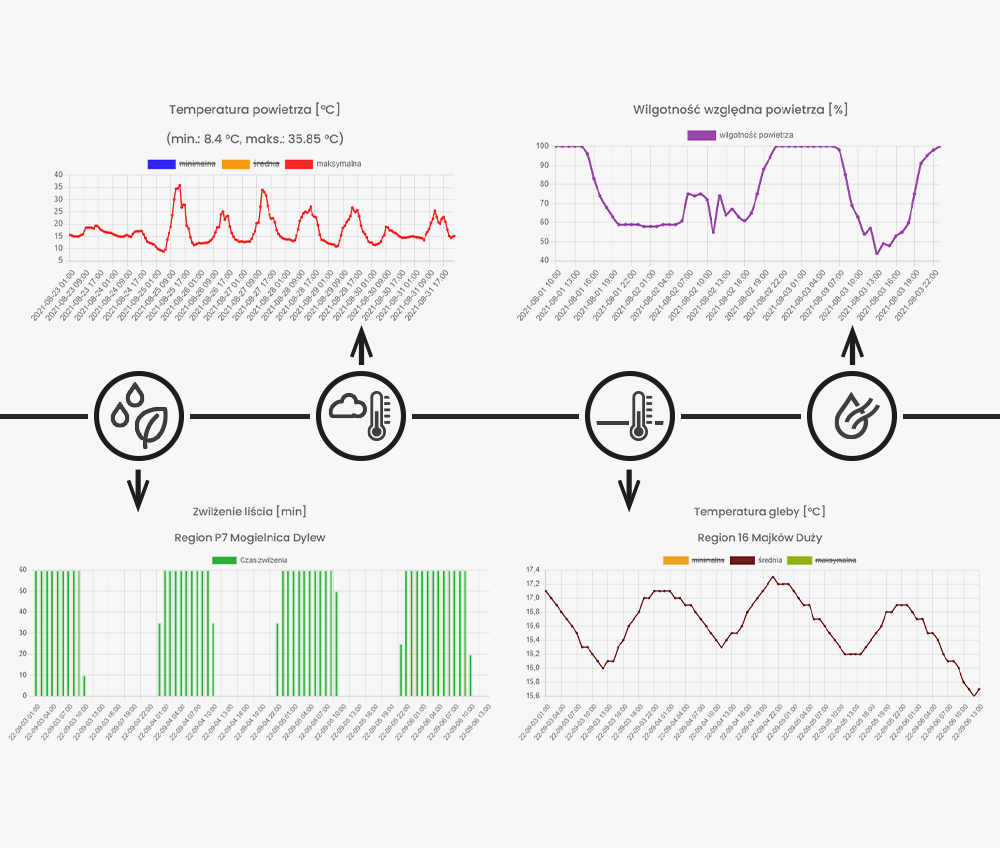
Meteorological Data
Access to current and historical data from the nearest weather station. The system displays data from each sensor that has been connected to the station, including air temperature and soil temperature, relative air humidity, amount of rainfall, leaf wetness time, as well as other parameters such as the Delta T indicator, which refers to water evaporation rate and is one of the main parameters determining the optimal conditions during spraying.
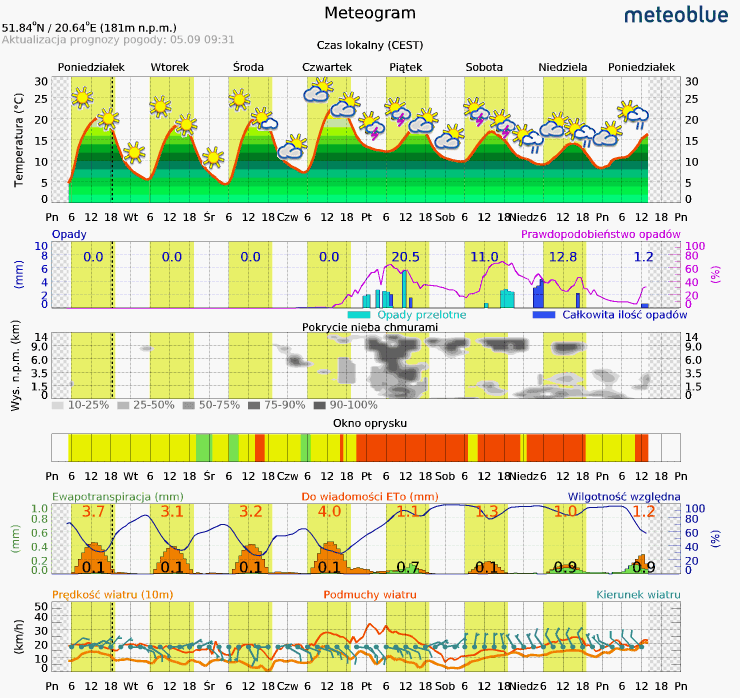
Weather Forecast
7-day weather forecast meteogram:
- Air temperature
- Precipitation probability
- Relative humidity
- Spray window – indicating the optimal conditions for protective treatments
- Eto (evapotranspiration) coefficient – all processes related to the outflow of water evaporating from the soil surface (evaporation) covered with vegetation (transpiration) to the atmosphere
- Cloud cover Wind speed and direction